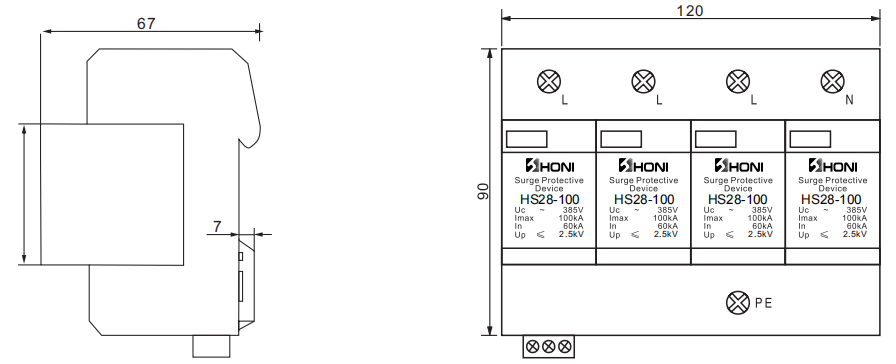
| Type Technical Data Maximum continuous voltage (UC) (L-N) | HS28-100 385 / 420V |
| Maximum continuous voltage (UC) (N-PE) | 275V |
| SPD to EN 61643-11 , IEC 61643-11 | Type 1+2 , class I+II |
| Lightning impulse current (10/350μs) (Iimp) | 15kA |
| Nominal discharge current (8/20μs) (In) | 60kA |
| Maximum discharge current (8/20μs) (Imax) | 100kA |
| Voltage protection level (Up) (L-N) | ≤ 2.5kV |
| Voltage protection level (Up) (N-PE) | ≤ 2.0kV |
| Response time (tA) (L-N) | < 25ns |
| Response time (tA) (N-PE) | < 100ns |
| Thermal Protection | YES |
| Operating State/Fault Indication | Green (good) / White or Red (replace) |
| Degree of protection | IP 20 |
| Insulating material / flammability class | PA66,UL94 V-0 |
| Temperature range | -40ºC~+80ºC |
| Altitude | 13123 ft [4000m] |
| Conductor Cross Section (max) | 35mm2 (Solid) / 25mm2 (Flexible) |
| Remote Contacts (RC) | Optional |
| Format | Pluggable |
| For mounting on | DIN rail 35mm |
| Place of installation | indoor installation |
Surge protection TRANSIENT VOLTAGE SURGES IN LV POWER LINES
Transient overvoltages are voltage surges that can reach tens of kilovolts with a duration of the order of microseconds.Despite their short duration, the high energy content can cause serious problems to equipment connected to the line, from premature aging to destruction, causing disruptions to service and financial loss.This type of surge can have various different causes, including atmospheric lightning directly striking the external protection (lightning rods) on a building or transmission line or the associated induction of electromagnetic fields on metallic conductors. Outdoor and longer lines are the most exposed to these fields, which often receive high levels of induction. It is also common for non-weather phenomena, such as transformer centre switching or the disconnection of motors or other inductive loads to cause voltage spikes in adjacent lines.
SURGES IN TELECOM AND SIGNALLING NETWORKS Surges tend to induce currents in all metal conductors; not only are the power lines affected, but so are all cables to a greater or lesser extent, depending on the distance to the focus of the surge. Although a lower current is induced, the effect produced is equally or more destructive, due to the greater sensitivity of electronic equipment connected to communications lines (telephone, Ethernet, RF, etc.).
IMPORTANCE OF THE GROUND CONNECTION Overvoltage protectors (SPD) divert excess energy to ground, so limiting the peak voltage to an acceptable value for connected electrical equipment. A ground connection in adequate condition is, therefore, a key aspect for effective protection against overvoltages. Monitoring ground connection condition guarantees proper operation of surge protection devices.
OUR SERVICE:
1.quick response in before sales period help you got order. 2.excellent service in production time let you know each step we made. 3.reliable quality solve you after sale headache. 4.long period quality warranty ensure you can buy without hesitate.
1. product design standard: this product is designed according to relevant international standards IEC, and its performance meets the requirements of national standard GB 18802.1-2011 "low voltage surge protector (SPD) part 1: performance requirements and test methods of surge protector for low voltage distribution system".
2. Scope of product use: GB50343-2012 Technical Code for Lightning Protection of Building Electronic Information System
3 Selection of surge protector: The primary SPD must be set in the main distribution box at the entrance of building power supply.
4. Product features: This product has the characteristics of low residual voltage, fast response speed, large current capacity (impulse current Iimp(10/350μs) is 25kA/ line, long service life, simple maintenance and convenient installation, etc.
5.Working temperature: -25℃ ~+70℃, working humidity: 95%.